Solar Overview
Solar PV System Descriptions
The REMPD documents material requirements for four types of solar PV systems: residential, commercial, utility PV (UPV) systems with crystalline silicon (c-Si) modules, or UPV systems with cadmium telluride (CdTe) modules. Silicon modules are assumed to contain monocrystalline passivated emitter and rear contact (PERC) cells, as this technology currently maintains the largest market share in the industry (Zuboy et al. 2022). We selected these system types and characteristics to represent a typical system in the given market sector that is consistent with those used in the annual NREL PV system cost benchmark (Ramasamy et al. 2021).
Further system characteristics are defined in Table 8, including the inverter loading ratio, which is used to convert direct current watts (WDC) to alternating current watts (WAC).
Table 8. REMPD Solar PV System Types and Characteristics
| PV System Type | Size | Module Type | Module Power | Module Size | Racking | Inverter Type | Inverter Loading Ratio |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
c-Si UPV |
100 MWDC |
c-Si PERC |
450 W |
2.2 m2 |
One-axis tracker |
Central, 0.5 MWAC |
1.28 |
|
CdTe UPV |
100 MWDC |
CdTe |
430 W |
2.47 m2 |
One-axis tracker |
Central, 0.5 MWAC |
1.28 |
|
Commercial rooftop |
200 kWDC |
c-Si PERC |
330 W |
1.7 m2 |
Ballast |
String, 20 kWAC |
1.15 |
|
Residential rooftop |
5.75 kWDC |
c-Si PERC |
330 W |
1.7 m2 |
Roof mount |
String, 5 kWAC |
1.15 |
In the REMPD, solar PV system materials are inventoried for the following components: PV modules, inverters, cabling, transformers, racking, and structural balance-of-system components. A typical utility PV system is illustrated in Figure 5. The organizational structure of system type, components, and subassemblies are provided in Table 9. The REMPD does not consider transportation and capital equipment required to install, maintain, operate, or decommission solar PV systems. All solar PV system material use is reported in units of kilograms per kilowatt of module rated capacity for ease of use across component and system types.
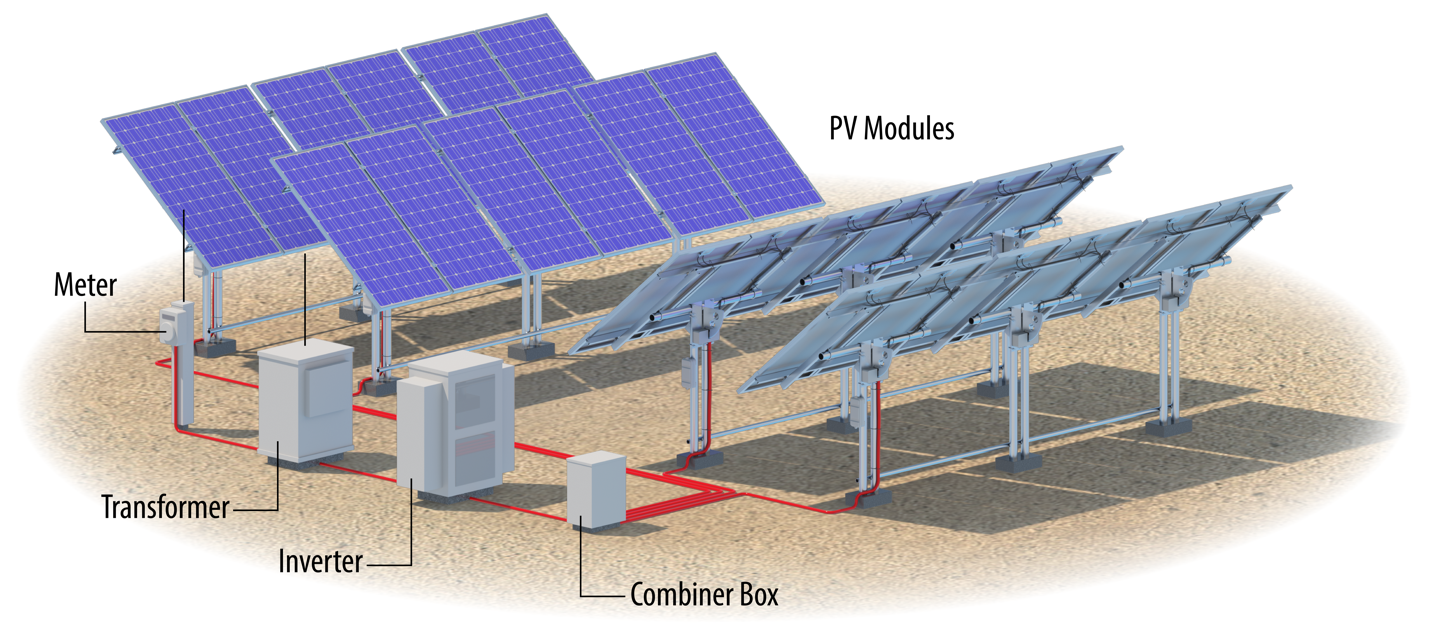
Table 9. REMPD Solar PV Component and Subassembly Organizational Structure
| System Type | Component | Subassembly | References for Material Quantities |
|---|---|---|---|
|
UPV types: Solar PV — c-Si UPV Solar PV — CdTe UPV |
PV module | Cell or absorber | Frischknecht et al. (2020) |
| Interconnect | |||
| Packaging | |||
| Frame | |||
| Diode | |||
| Inverter | General inverter | Jungbluth et al. (2012) | |
| Printed board assembly | |||
| Transformer | Transformer | Antonanzas et al. (2019) | |
| Cabling | Cabling | Frischknecht et al. (2020) | |
| Racking | Tracker support | Antonanzas et al. (2019) | |
| Tracker motor | |||
| Tracker battery | |||
| Tracker minimodule | |||
| Remaining structural balance of system | Fence | Antonanzas et al. (2019) and Sinha and de Wild-Scholten (2012) | |
| Conduit | |||
| Inverter foundation | |||
|
Rooftop types: Solar PV — Commercial Rooftop Solar PV — Residential Rooftop |
PV module | Cell | Frischknecht et al. (2020) |
| Interconnect | |||
| Packaging | |||
| Frame | |||
| Diode | |||
| Inverter | General inverter | Tschümperlin et al. (2016) | |
| Printed board assembly | |||
| Cabling | Cabling | Frischknecht et al. (2020) | |
| Racking |
Rooftop racking (Commercial: ballast); (Residential: roof mount) |
Frischknecht et al. (2020) |
An abridged overview of the main materials by component are:
- PV modules. The primary cell or absorber materials are silicon or cadmium telluride, whereas the interconnect materials are copper, tin, and lead. The packaging includes ethylene vinyl acetate, glass (solar-grade rolled glass or float), a laminate of polyethylene and polyvinylfluoride, and finally silicone sealant and glass-reinforced plastic for diode housing. The module frame is made from an aluminum alloy primarily with magnesium. The diode primarily contains molybdenum, copper, and glass along with silicon, tin, lead, and epoxy resin.
- Inverters. The largest masses of material in the housing are steel, copper, aluminum, and plastics. Other major materials are the compounds and chemicals embedded in the printed boards and their components, which are numerous.
- Transformers. Primarily rely on concrete, ferrite, transformer oil, copper, steel, plastic, and epoxy resin.
- Cabling. Copper conductors and polymer insulating material (e.g., polypropylene).
- Racking. Trackers are largely comprised of steel, zinc, and aluminum as well as chromium steel, with some reliance on copper and specialty compounds for the battery including lithium as well as PV module materials used for dedicated tracker power. Rooftop racking types primarily rely on aluminum and polyethylene structures, along with a small amount of steel components.
- Remaining structural balance of system. Includes polyvinylchloride conduit, steel, concrete, and zinc coatings for fencing, and concrete foundations for inverters.
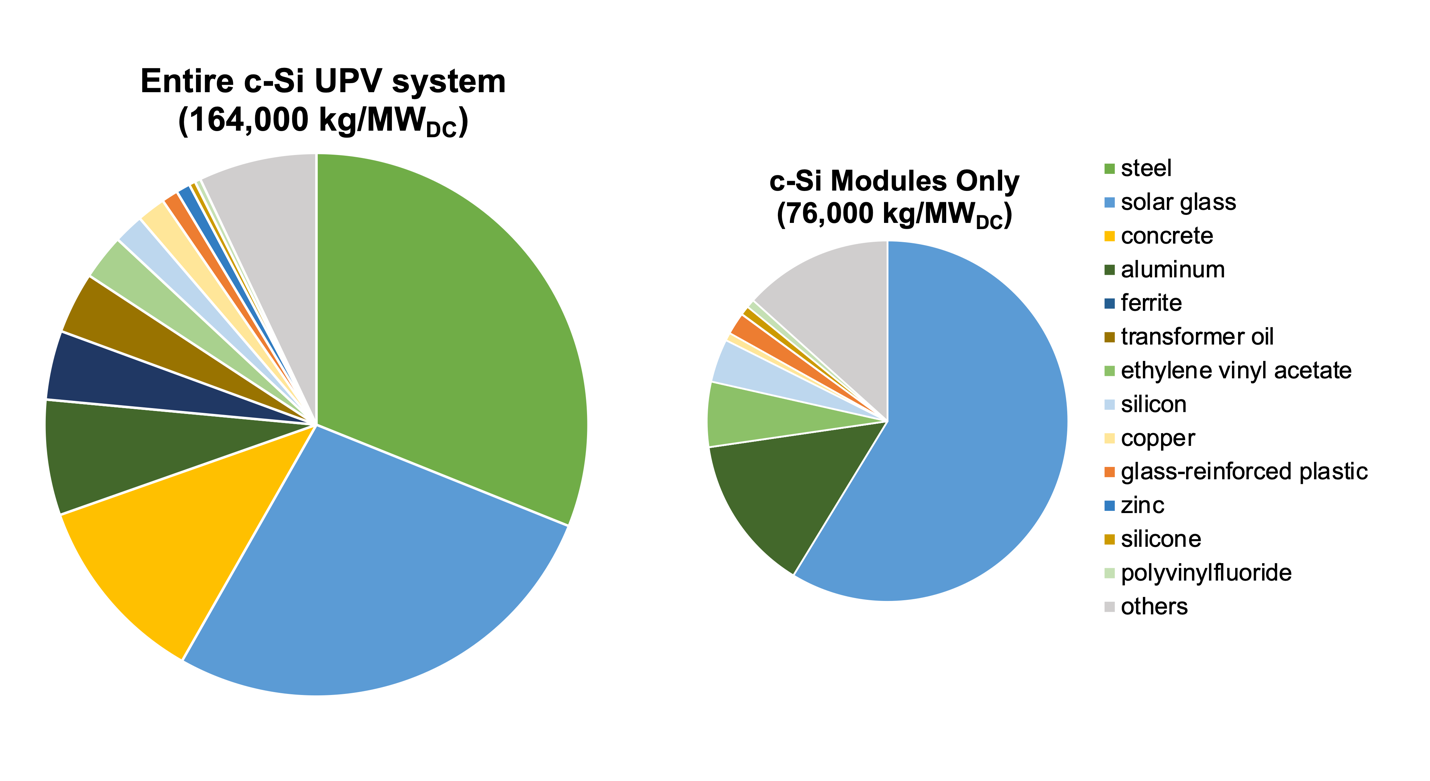
A breakdown of typical material quantities in a c-Si UPV system is shown in Figure 6.